Cast Iron Welding Consumables Introduction-Covered Electrodes
1.Parent Material Properties:
Cast Iron contains carbon (C): 2 ~ 4%、Si:0.5 ~ 4%、Mn:0.3 ~ 2%、P:0.05 ~ 1%; the iron-based alloy casting. It applies for a special purpose with additional content of Mn, Si, Ni, Cr or Mo alloys, but worse toughness and weldability. Common cast iron classification is shown in the table below:
|
category |
JIS Chapter |
JIS Code |
Characteristics |
|||
|
Gray Cast Iron |
General cast iron |
G5501 |
FC100 FC150 FC200 |
①All purpose for industries, well-known named with broken surface in gray color. ②High-grade cast iron comprised of Pearlite structure; the higher strength and toughness than general cast iron. |
||
|
High-grade cast iron |
G5501 |
FC250 FC300 FC350 |
||||
|
Nodular cast iron |
Nodular cast iron |
G5502 |
FCD350 FCD400 FCD450 FCD500 FCD600 FCD700 FCD800 |
①Also named ductile iron or nodular cast iron. Generally add Mg, Ce or Ca in the composition of the original spheroidizing graphite cast iron. ②Tensile strength is a 2-3 times of general cast iron; the higher elongation and well weldability. |
||
|
Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) |
G5503 |
FCAD900 FCAD1000 FCAD1200 FCAD1400 |
||||
|
Ferritic nodular cast iron |
G5504 |
FCAD300LT (Low temperature use) |
||||
|
Malleable Cast Iron |
blackheart malleable cast iron |
G5702 |
FCMB270 FCMB310 FCMB340 FCMB360 |
①Blackheart malleable cast iron is originally made of whiteheart malleable cast iron by heating at 700~900℃ to dissolve Cementite into graphitization so as to be capable of toughness in Ferrite with the black broken surface. ②Whiteheat malleable cast iron is to heat the white pig iron at 850-1000℃ into oxidizing phenomenon for decarbonization that improves thoughness. ③Pearlite malleable cast iron is formed into graphite and pearlite structure by heating process that performs better in cutting, wearing, strength, and quenching. cutting, wearing |
||
|
whiteheart malleable cast iron |
G5703 |
FCMW300 FCMW370 FCMWP440 FCMWP490 FCMWP540 |
||||
|
Pearlite malleable cast iron |
G5704 |
FCMP440 FCMP490 FCMP540 FCMP590 FCMP690 |
||||
|
Alloy Cast Iron |
Ni-alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Resistance of heat, corrosion, and wearing. |
||
|
Cr-alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Hardening, wearing and heating resistances |
|||
|
Ni-Cr alooy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Alloy cast iron is the most use, high strength, toughness, hardness, heat and corrosion resistances. |
|||
|
Ni-Cr-Mo alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
High strength, fatigue and wear resistances generally use for engine crankshaft. |
|||
|
Ni-Cr-Si alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Heat resistance generally use for stove metalware. |
|||
|
Ni-Cr-Cu alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Heat and acid resistance. |
|||
|
Al-alloy cast iron |
-- |
-- |
Heat and acid resistance generally use for boiler accessories. |
|||
2.Welding method and characteristics:
It is due to the high content of carbon, poor weldability, and even to difficultly weld for cast iron alloy. The common problems on welding are cracking and blowholes, and therefore, should avoid to.
①Hard and brittle white pig rod martensitic structure composition may cause cracking phenomenon.
②Cementite and graphite are both dissolved and oxidized after heating with high temperature that it causes with a large amount of CO or CO2 gas resulting in blowholes.
In Cast iron welding process, the preheat temperature can be classified high-temp. and low-temp. on welding. High temperature preheat is at 500 ~ 600℃ in whole parent material and then welding afterwards. Generally, it applies for oxyacetylene welding or electrode welding; the large deformation of workpiece and longer waiting time of preheat as disadvantage. Low temperature preheat at the welding part is at 100 ~ 200℃ and then welding afterwards. It applies for electrode welding, argon welding or gas metal arc welding (GMAW); the smaller deformation of workpiece but the brittleness at HAZ.
In order to weld effective combined with parent material, cast iron workpiece on welding artwork the common applications are recommended as follows:
①Embedded board & Bar filling:
In order to increase the strength of the weld filling, the cast iron filling and welding parts embedded with steel material, steel bar as reinforcement; the recommended welding consumable of ENiFe-CI.

②Implant bolts:
Implant bolts prior to welding; weld the bolts around to the entire weld.
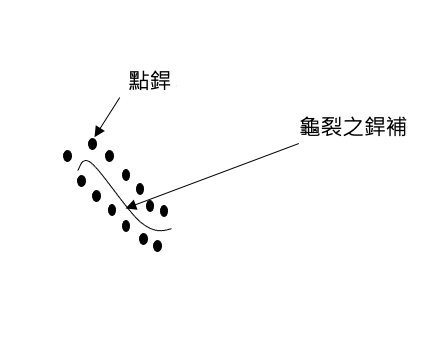
③Drilling cracking holes:
In order to prevent the cracks continuous and expanding, and therefore, it is required to drill a hole at each side of the crack and then wear it in an arc groove and fill it up.

④Coating:
The cracking is usually caused near the melting interface and HAZ. Welding a dual coatings with Eni-Ci grade material at the groove surface and then fill it up afterwards for the welding difficulty on workpieces.

⑤Hammering:
Repeatedly hammering on the deformed weld after welding is for the stress relief. The head of the hammer must be blunt head in order to prevent the stress concentration for cracks, but not recommended for the bottom weld or surface weld.
⑥Cracks on each side of spot welding:
Gray cast iron welding is to spot welding on each side of the crack by a short distance between so as to release the stress and then weld it; grinding the spot welding part off at the end.